Unlocking the Mysteries of Tardigrades: How Tiny Creatures Survive the Impossible
Unlocking the Mysteries of Tardigrades: How Tiny Creatures Survive the Impossible
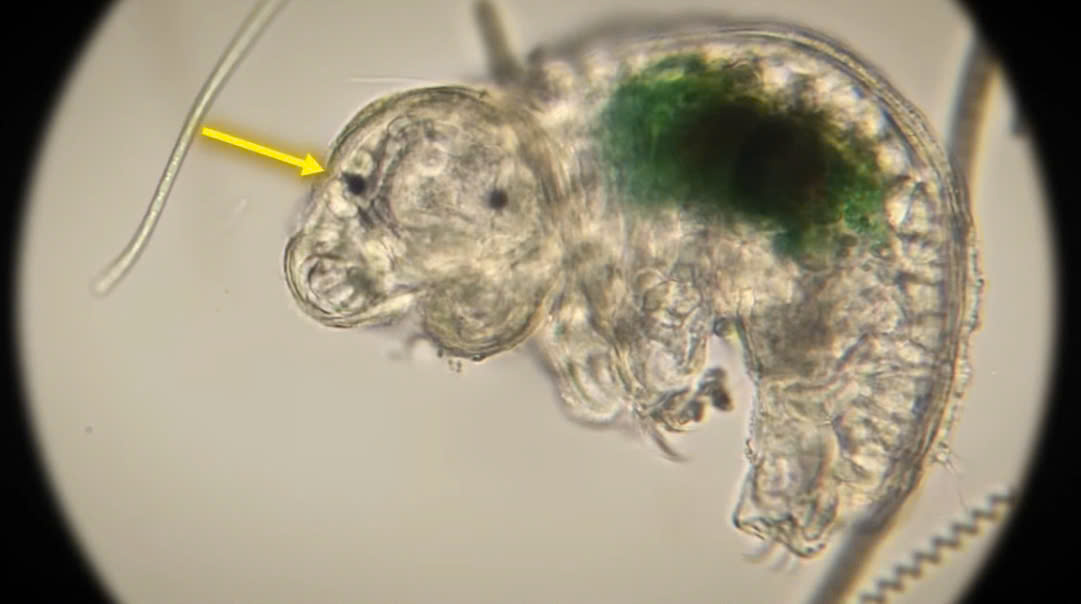
2. Unique Body Structure: Tardigrades have a distinct body structure that differs from most other animals. They have lost several genes related to the development of a traditional head-to-tail body form. Instead, their bodies are largely composed of head-like segments, making their entire form homologous to just the head region of other arthropods. This adaptation is a result of their evolutionary history and unique development.
3. Radiation Resistance: Research indicates that tardigrades can withstand about 1,000 times more radiation than humans. They exhibit this resilience in both active and dormant states. The radiation resistance is surprising given that ionizing radiation’s indirect effects are generally intensified in the presence of water. Tardigrades’ ability to avoid DNA damage and efficiently repair it is thought to contribute to their survival and reproduction even after severe radiation exposure.
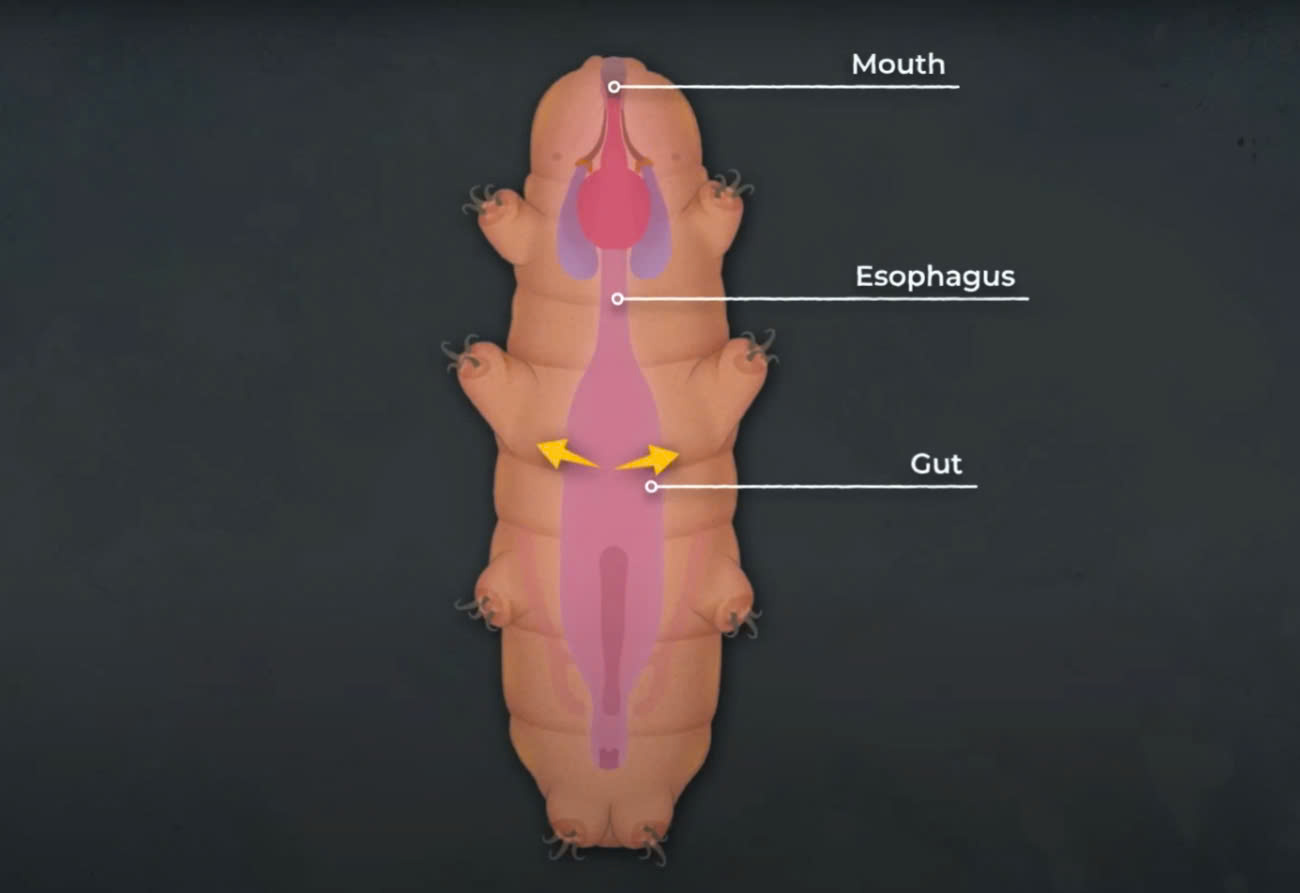
3. Feeding Habits: Tardigrades feed by extracting fluids from cells. They possess specialized mouthparts called stylets that can puncture cells and allow them to suck out the internal liquids. Their diet is diverse, including plant cells, bacteria, algae, fungi, protozoa, nematodes, and even other tardigrades. This feeding behavior helps control populations of various microorganisms in their environments.
4. Distinct Phylum: Tardigrades constitute their own phylum, making them unique in the animal kingdom. They represent a taxonomic rank just below Kingdom, with over a thousand known species living in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial habitats. This classification underscores their evolutionary significance and the diversity within this ancient lineage.
Tardigrades’ extraordinary abilities make them a subject of ongoing scientific study, particularly in fields related to extreme environments and potential space colonization. Their survival strategies offer valuable insights into resilience and adaptation, contributing to broader understandings of life’s potential across various conditions.