Sumerians Looked To The Heavens As They Invented The System of Time… And We Still Use It Today
Sumerians Looked To The Heavens As They Invented The System of Time… And We Still Use It Today
One might find it curious that we divide the hours into 60 minutes and the days into 24 hours – why not a multiple of 10 or 12? Put quite simply. The answer is because the inventors of time did not operate on a decimal (base-10) or duodecimal (base-12) system but a sexagesimal (base-60) system. For the ancient Sumerian innovators who first divided the heavens’ movements into countable intervals, 60 was the perfect number.
One might find it curious that we divide the hours into 60 minutes and the days into 24 hours – why not a multiple of 10 or 12? Put quite simply. The answer is because the inventors of time did not operate on a decimal (base-10) or duodecimal (base-12) system but a sexagesimal (base-60) system. For the ancient Sumerian innovators who first divided the heavens’ movements into countable intervals, 60 was the perfect number.
The Useful Number 60
The number 60 can be divided by 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, and 30 equal parts. Moreover, ancient astronomers believed there were 360 days in a year, of which 60 fit neatly into six times. The Sumerian Empire did not last. However, for more than 5,000 years, the world has remained committed to delineating time.
The Passage of Time
Many ancient civilizations had a rough approximation of the passage of time. A day began when the sun rose, and night began at sunset. Somewhat less obvious were weeks, months, and years; however, ancient peoples had approximated these two. A month was the length of time of one complete lunar cycle, whereas a week was the length of time for one phase of the lunar cycle. A year could be estimated based on the changing seasons and relative position of the sun. Once the sun’s zenith was determined, scholars could count the number of sunrises/sunsets that passed until it reached its zenith again. In this manner, the ancient Egyptians, Mayans, and Babylonians, among others, determined that the year had 360 days. Yet it was the Sumerian astronomers and mathematicians who first systematically divided the passage of time. Their work was widely accepted and spread throughout Eurasia.
The Decimal System Was Not the First System for Counting
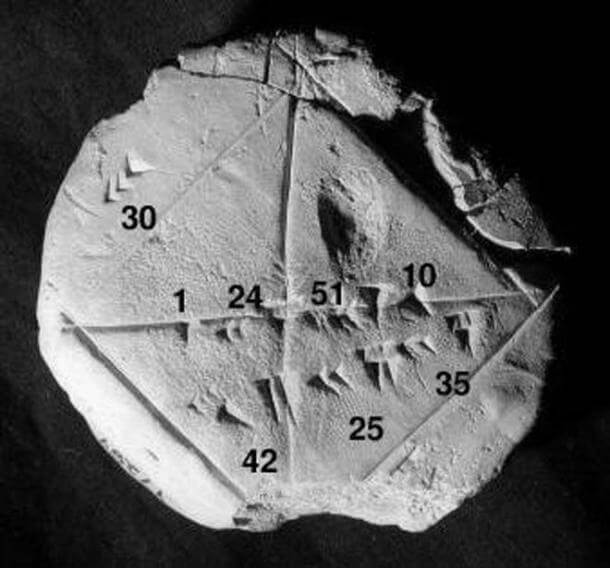
The decimal system is today the most widely used numerical base. It is a readily available counting system, given that humans have ten fingers on which to count. As such, there are several claimants to the invention of the decimal system, notably the Greeks (circa 300 BC), the Chinese (100 BC), and the Indians (circa 100 AD). Less well-known are the origins of the duodecimal system. However, it appears to have arisen independently in ancient Nigerian, Chinese, and Babylonian languages, markedly in the belief of the 12 signs of the zodiac. However, all of these were preceded by the ancient Sumerians, who crafted their sexagesimal system in the 3rd millennium BC.
The Sumerian Invention of the Sexagesimal System
The Sumerians initially favored the number 60 because it was so easily divisible. Not only were there few remainders when working with the number 60 and its multiples, but the remainders that did appear also did not have repeating decimals (ex. 1/3 = 0.333…), a concept Sumerians could not process at the time. The land of Sumer was conquered in 2400 BC by the Akkadians and then by the Amorites (also known as the Babylonians) in 1800 BC. Each subsequent ruling power also appreciated the user-friendly sexagesimal system and incorporated it into their mathematics. So the notion of dividing time into units of 60 persisted and spread to the East in Persia, India, and China and to the West in Egypt, Carthage, and Rome. The system neatly complemented the Chinese astronomers’ work of discovering the 12 astronomical hours of the stars (a mostly theoretical discovery as most people lived by the sun). It also worked with imperial military strategies, particularly the night watch division into multiple even increments. The Egyptians maintained three watches each night. The Romans had four.
With Greek and Islamic innovations in geometry, it was discovered the 360 was not only the length of time of the earth’s ideal orbit but the perfect measurement of a circle. The sexagesimal system thus began to solidify its place in history by becoming essential for mathematics and navigation (the earth is divided into degrees of longitude and latitude). Finally, with the invention of the timepiece in the 14th century, the circular clock face was divided into neat, sexagesimal quadrants that gave each minute 60 seconds.